VizCommender: Computing Text-Based Similarity in Visualization Repositories for Content-Based Recommendations
Abstract
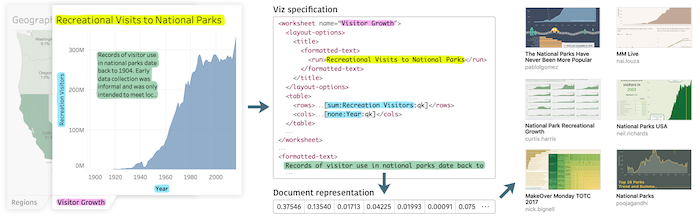
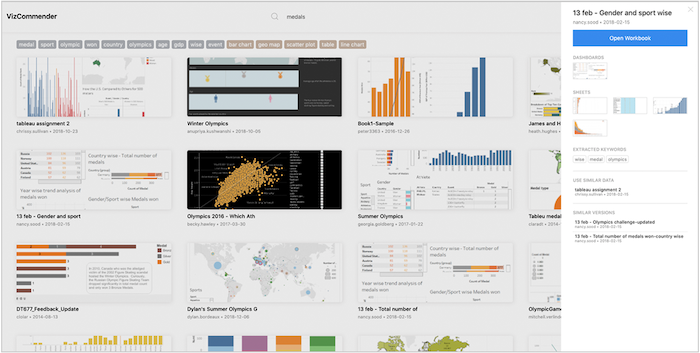
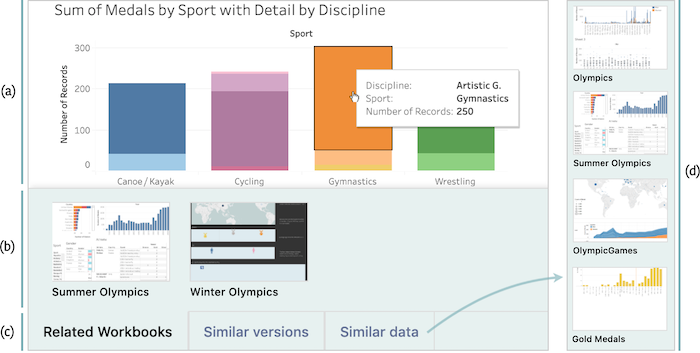
Cloud-based visualization services have made visual analytics accessible to a much wider audience than ever before. Systems such as Tableau have started to amass increasingly large repositories of analytical knowledge in the form of interactive visualization workbooks. When shared, these collections can form a visual analytic knowledge base. However, as the size of a collection increases, so does the difficulty in finding relevant information. Content-based recommendation (CBR) systems could help analysts in finding and managing workbooks relevant to their interests. Toward this goal, we focus on text-based content that is representative of the subject matter of visualizations rather than the visual encodings and style. We discuss the challenges associated with creating a CBR based on visualization specifications and explore more concretely how to implement the relevance measures required using Tableau workbook specifications as the source of content data. We also demonstrate what information can be extracted from these visualization specifications and how various natural language processing techniques can be used to compute similarity between workbooks as one way to measure relevance. We report on a crowd-sourced user study to determine if our similarity measure mimics human judgement. Finally, we choose latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) as a specific model and instantiate it in a proof-of-concept recommender tool to demonstrate the basic function of our similarity measure.
Video
Publication
VizCommender: Computing Text-Based Similarity in Visualization Repositories for Content-Based Recommendations.
IEEE Trans. on Visualization and Computer Graphics (TVCG), 27(2): 495-505, 2021
IEEE Trans. on Visualization and Computer Graphics (TVCG), 27(2): 495-505, 2021
Tags
Industry Collaborator